Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-09-05 Origin: Site
Faucet supply lines may be small components in your plumbing system, but they play a vital role in delivering water efficiently and reliably to your fixtures. Whether you’re installing a new kitchen faucet, replacing bathroom sink water supply lines, or upgrading toilet water lines, choosing the right faucet and hose combination ensures durability, leak prevention, and proper water flow.
This guide explains everything you need to know about faucet supply lines—sizes, materials, installation, and maintenance—so you can select the correct faucet feed line for any application.

Table of Contents
Faucet supply lines, also known as faucet water lines or faucet feed lines, are flexible or rigid tubes that connect your faucet to the shut-off valve on the wall. They deliver hot and cold water from the main plumbing system to your sink or toilet.
These water supply lines come in a variety of lengths, diameters, and materials to accommodate different fixtures, including kitchen sink hoses, bathroom sink water lines, and toilet supply line sizes.

Water Delivery: Supply lines transport water from the shut-off valve to faucets, sprayers, or toilets.
Pressure Management: Proper faucet pipe diameter ensures strong water pressure without flow restrictions.
Flexibility & Installation: Flexible sink supply lines make installation easier in tight spaces.
Leak Prevention: Correct threading and high-quality connectors prevent leaks over time.
Compatibility: Matching supply line size to your faucet and fixture avoids performance issues.

Braided Stainless Steel – Strong, corrosion-resistant, and the most durable option for kitchen faucet supply lines.
Braided Nylon – Lightweight and flexible, often used for bathroom sink water supply lines.
PVC or Plastic Tubing – Budget-friendly but less durable.
Copper Lines – Rigid and long-lasting, suitable for high-pressure water systems.
Choosing the right water supply line depends on both length and diameter.
3/8 Supply Line – The most common size for bathroom sink water supply lines.
1/2 Inch Supply Line – Frequently used for kitchen sink water lines or high-flow faucets.
5/8 Inch – Used in some specialty or commercial applications.
12 inches – Compact spaces like pedestal sinks.
16 inches – Standard bathroom sink water lines.
20 inches – Popular for both kitchens and bathrooms.
24–30 inches – Longer runs, such as when connecting dishwasher supply line size to plumbing.
| Pipe Diameter | Typical Use | Flow Rate (GPM) |
| 3/8 inch | Bathroom sink faucets | Up to 20 GPM |
| 1/2 inch | Kitchen sink supply lines | 20–30 GPM |
| 5/8 inch | High-flow or specialty faucets | 30+ GPM |
| 3/4 inch | Main residential supply | Multi-fixture |
| 1 inch+ | Larger homes & commercial buildings | Very high flow |

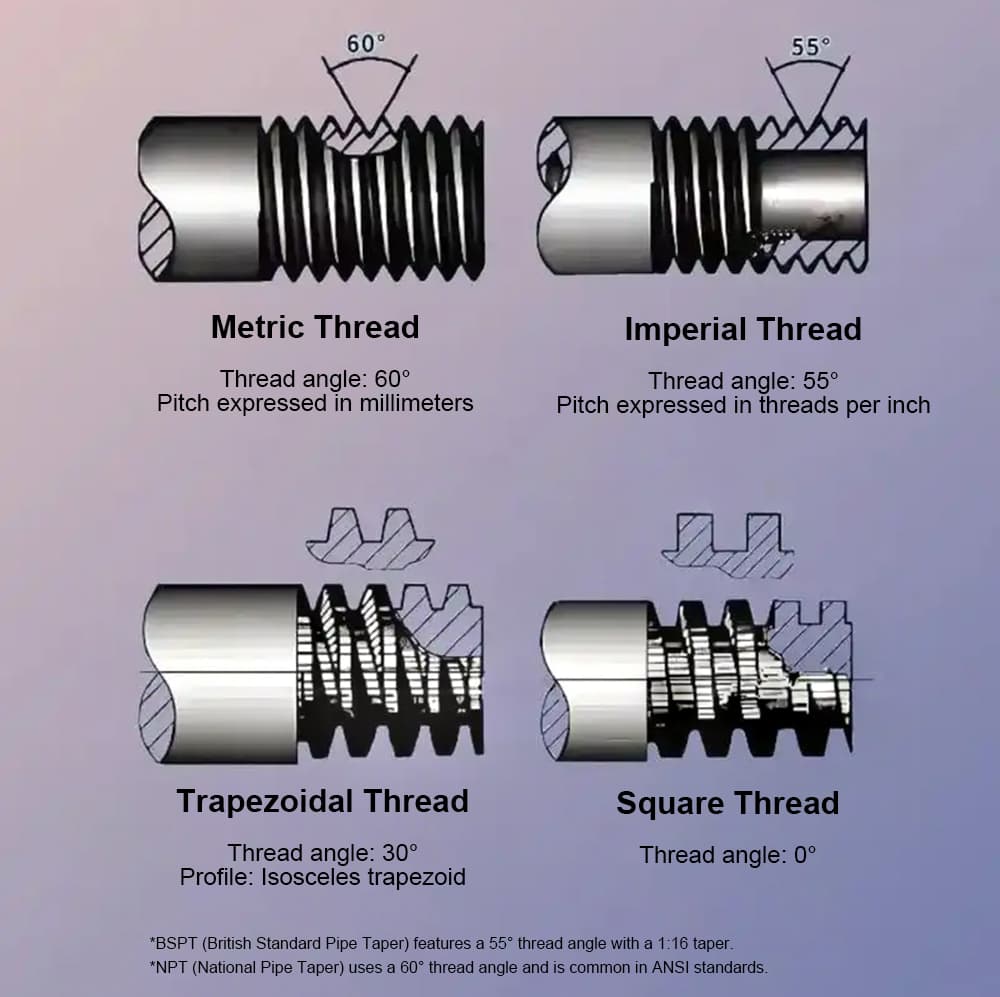
NPT (National Pipe Thread): Standard in the U.S., tapered threads ensure leak-tight seals.
BSPT (British Standard Pipe Thread): Common internationally; slightly different taper angle.
NPS (National Pipe Straight): Requires a gasket or O-ring for sealing.
ISO Standards: Used in global applications for compatibility.
Understanding threading is critical when working with sink sprayer connection types, sink water intake hose adapters, or international faucets.
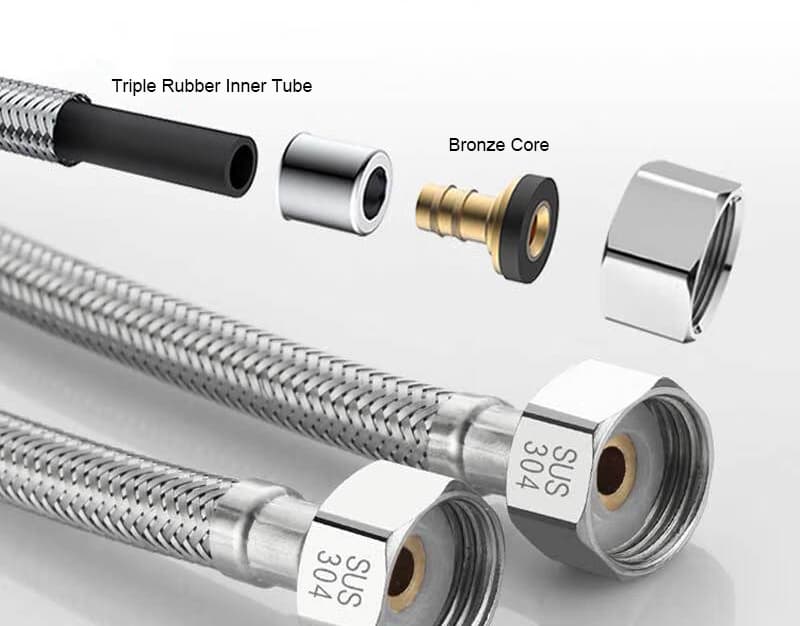

Identify connection points under the sink.
Measure male threads (OD) or female threads (ID) with a ruler or caliper.
Check nominal sizes (e.g., 3/8 or 1/2 inch).
Measure length from shut-off valve to faucet inlet.
Confirm connector type (compression vs threaded).
Consult manufacturer specs for faucet-specific requirements.
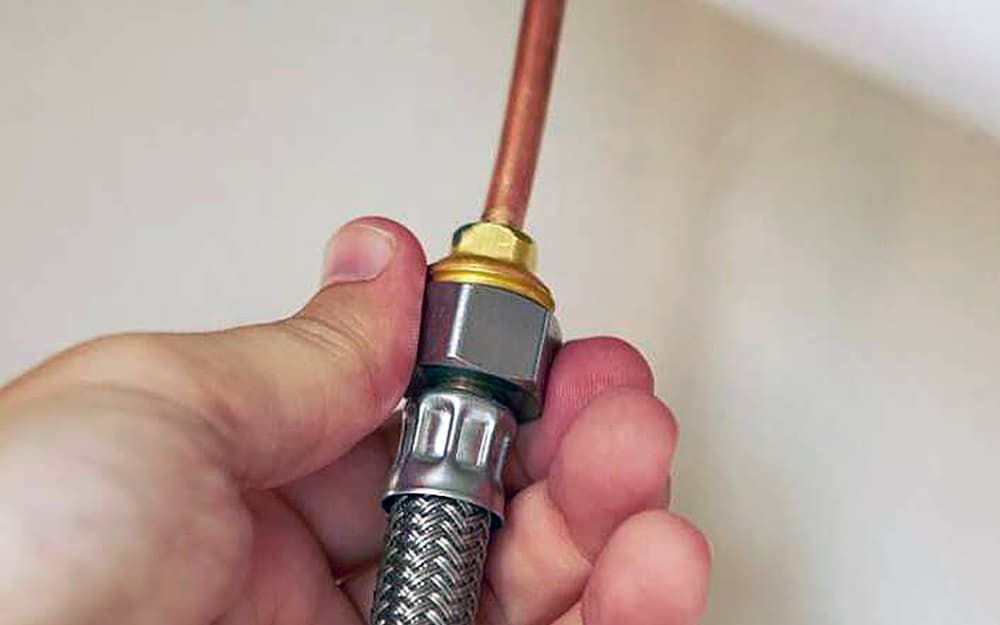

Flow Rate Needs: Kitchen faucets may need larger kitchen sink water supply lines, while bathroom sinks typically use 3/8 inch.
Faucet Type: Verify whether you need transactional faucet supply lines for replacement or new installation.
Connector Types: Match shut-off valve and faucet fittings to avoid leaks.
Appliance Compatibility: Ensure the right dishwasher supply line size or toilet water line size is selected.
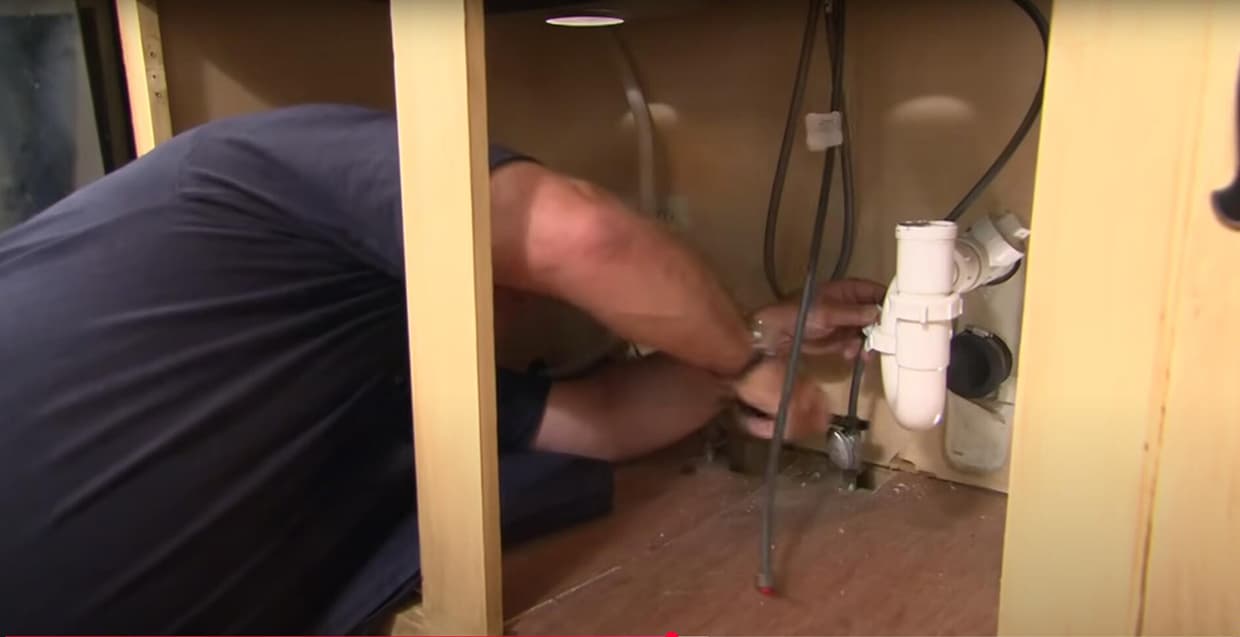

Turn off water supply at shut-off valves.
Remove old faucet lines with a wrench.
Wrap threads with Teflon tape for a leak-proof seal.
Connect faucet and hose by hand first, then tighten with a wrench.
Avoid kinks in flexible kitchen sink hoses or bathroom sink water supply lines.
Flush faucet lines before final use to remove debris.
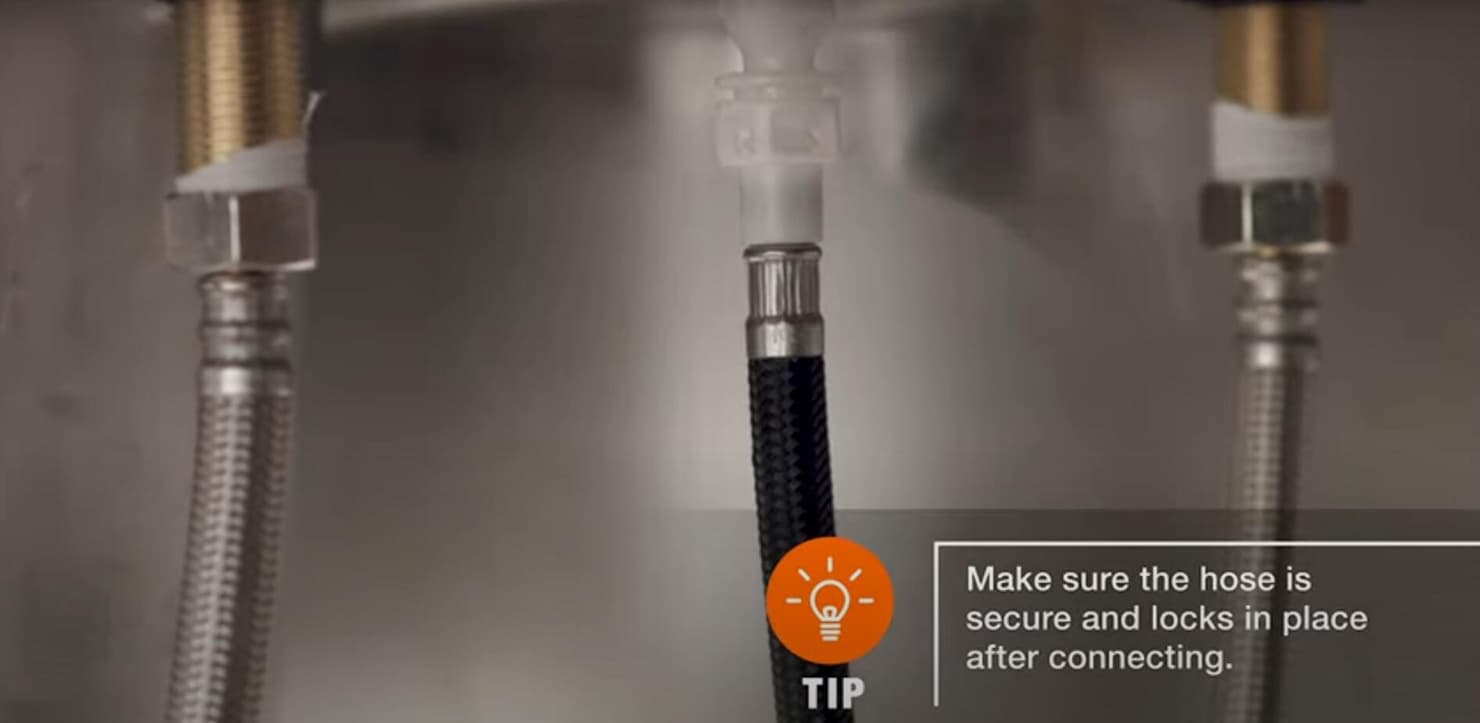

Inspect regularly for leaks or corrosion around faucet lines.
Flush supply lines every 6–12 months.
Replace old supply lines every 5–10 years, especially braided nylon or PVC types.
Check shut-off valves to ensure they operate properly during emergencies.

The right faucet supply lines are essential for reliable performance, leak prevention, and efficient water delivery in both kitchens and bathrooms. Whether you’re selecting kitchen faucet supply lines, a toilet water line size, or a sink sprayer connection type, always measure carefully, match connector types, and follow faucet manufacturer specifications.
With proper selection, installation, and maintenance, your faucet water lines will ensure years of dependable service in your home plumbing system.
Q: Is PEX safe for hot water applications?
A: Initially, PEX was met with some concerns regarding its safety for potable water. However, modern PEX pipes are tested and certified to meet NSF/ANSI Standard 61, the official standard for drinking water system components. This certification ensures that PEX pipes do not leach harmful chemicals into the water at levels that pose a health risk to consumers.
